Welcome to the realm of NEC Chapter 9 Table 8, an indispensable resource for electrical professionals. This comprehensive guide will delve into the significance, applications, and impact of this crucial table on electrical design and installation practices.
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 provides a detailed breakdown of ampacity ratings for various cable types, enabling engineers to select appropriate conductors for safe and efficient electrical systems. By understanding the principles and calculations associated with this table, electrical professionals can optimize system design, ensure compliance with industry standards, and enhance overall electrical safety.
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8: Basic Principles

NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 serves as a fundamental reference for electrical professionals, providing essential guidelines for grounding and bonding systems. It establishes the minimum requirements to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
The table is organized into several categories and subcategories, each addressing specific aspects of grounding and bonding:
Grounding
- System Grounding: Defines the methods for connecting the electrical system to the earth, ensuring a low-resistance path for fault currents.
- Equipment Grounding: Artikels the requirements for grounding non-current-carrying metal parts of electrical equipment, protecting individuals from electrical shocks.
- Bonding: Specifies the techniques for electrically connecting different parts of the grounding system, ensuring continuity and minimizing impedance.
NEC Chapter 9 Key Principles
The application of NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 is guided by several key principles:
- Safety: The primary objective is to protect individuals from electrical hazards, ensuring the safety of electrical installations.
- Reliability: The guidelines promote the reliability of electrical systems by preventing faults and minimizing downtime.
- Uniformity: The table establishes consistent requirements across the industry, ensuring uniformity in the design and installation of grounding and bonding systems.
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8: Calculations and Applications

NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 provides a comprehensive set of calculations and applications that electrical professionals use to design and install electrical systems. The table includes formulas for determining cable ampacity, voltage drop, and other electrical parameters.
Cable Ampacity
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 can be used to determine the ampacity of a cable, which is the maximum current that the cable can safely carry. The ampacity is determined by the cable’s size, type, and insulation. The table also includes correction factors that can be used to adjust the ampacity for different conditions, such as temperature and number of conductors in a raceway.
Voltage Drop
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 can also be used to calculate the voltage drop in a circuit. The voltage drop is the difference between the voltage at the source and the voltage at the load. The voltage drop is caused by the resistance of the conductors in the circuit. The table includes formulas for calculating the voltage drop for different types of circuits.
Other Applications
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 can also be used for a variety of other applications, such as:
- Determining the size of a conduit
- Calculating the number of conductors in a raceway
- Estimating the cost of an electrical installation
Limitations and Considerations
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 is a valuable tool for electrical professionals, but it is important to be aware of its limitations and considerations. The table is only applicable to certain types of cables and circuits. It is also important to use the table correctly and to follow all of the instructions provided in the NEC.
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8: Comparison to Other Standards
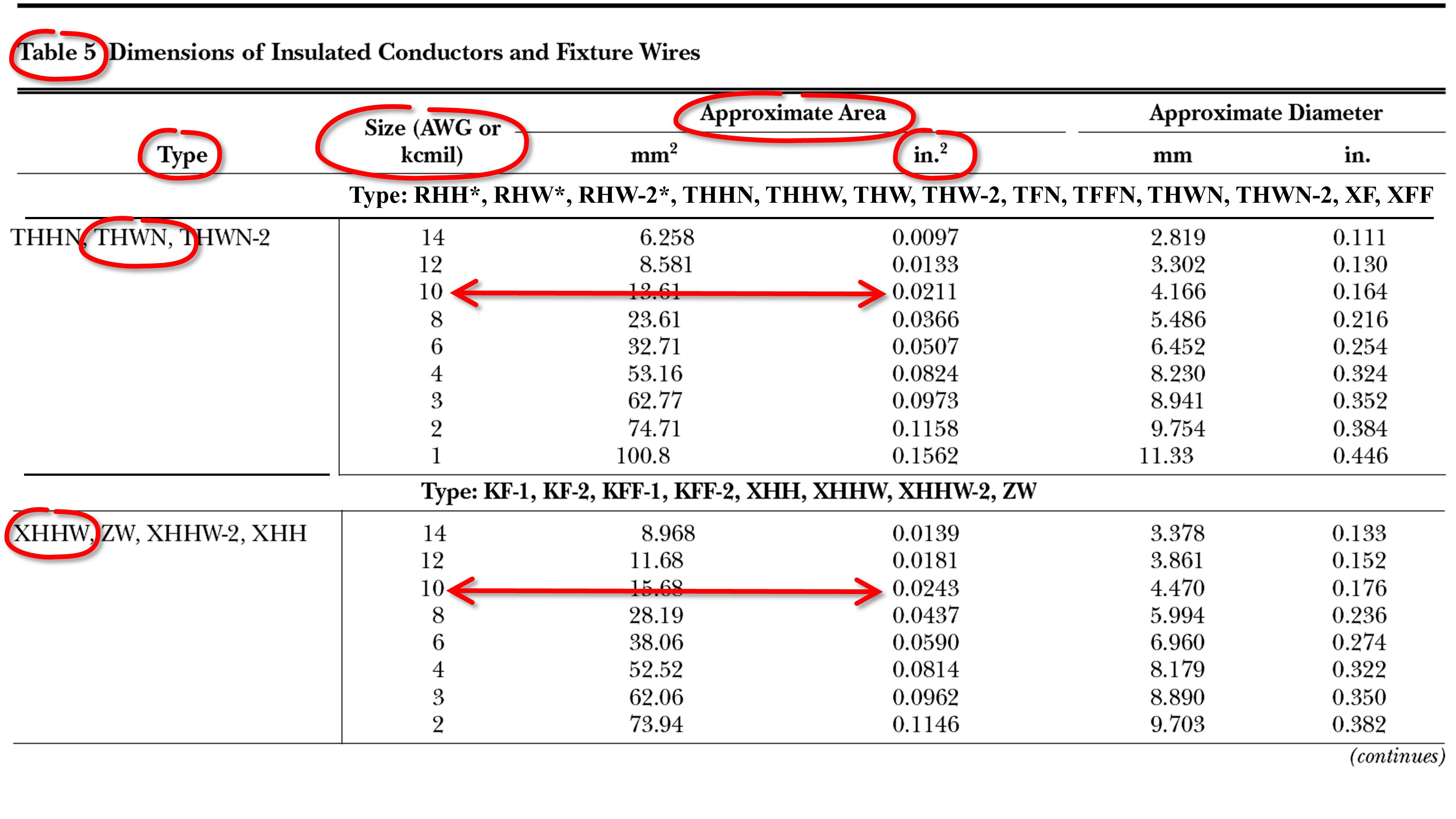
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 provides basic principles and calculations for grounding and bonding electrical systems. It is important to note that NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 is not the only standard that addresses grounding and bonding. Other electrical standards, such as the IEC and UL, also have similar tables.
While these tables share many similarities, there are also some key differences. One of the most notable differences is the way that the tables are organized. NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 is organized by grounding electrode system type, while the IEC and UL tables are organized by system voltage.
Another key difference is the way that the tables calculate grounding electrode resistance. NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 uses a simplified formula that assumes that the grounding electrode is a single rod or pipe. The IEC and UL tables, on the other hand, use more complex formulas that take into account the type of grounding electrode and the soil conditions.
These differences can have a significant impact on the design and installation of electrical systems. For example, the simplified formula used in NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 may not be accurate for systems with complex grounding electrode systems. As a result, it is important to consult with a qualified electrician when designing and installing electrical systems.
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8: Impact on Electrical Design
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 has a significant impact on electrical design practices, influencing the selection of cable sizes, conduit sizes, and other electrical components. It provides essential guidelines for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems.
Influence on Cable Selection
The table specifies the ampacity ratings of different cable types based on their construction, insulation, and operating conditions. By referring to the table, electrical designers can determine the appropriate cable size for a given load, ensuring that the cable can safely carry the required current without overheating or causing insulation failure.
Impact on Conduit Sizing, Nec chapter 9 table 8
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 also provides guidelines for determining the minimum size of conduit required for a given number of cables. This information is crucial for ensuring that cables are properly protected from physical damage and that heat dissipation is adequate. By following the table’s recommendations, designers can avoid conduit overcrowding, which can lead to overheating and insulation breakdown.
Optimization of Electrical System Design
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 can be used to optimize electrical system design by ensuring that components are properly sized and coordinated. By carefully considering the ampacity ratings and conduit requirements, designers can minimize the use of oversized components, which can result in cost savings and improved system efficiency.
Final Thoughts: Nec Chapter 9 Table 8

In conclusion, NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 serves as a fundamental reference for electrical professionals, guiding them in the design and installation of safe and efficient electrical systems. Its comprehensive nature and wide-ranging applications make it an essential tool for ensuring compliance with industry standards and safeguarding electrical installations.
General Inquiries
What is the significance of NEC Chapter 9 Table 8?
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 provides ampacity ratings for various cable types, enabling electrical professionals to select appropriate conductors for safe and efficient electrical systems.
How is NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 used in electrical design?
Electrical engineers use NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 to determine the ampacity of cables, ensuring that they are appropriately sized to carry the required electrical current.
What are the limitations of NEC Chapter 9 Table 8?
NEC Chapter 9 Table 8 does not account for all factors that may affect cable ampacity, such as ambient temperature, installation methods, and derating factors.